DEBUNKING ROTATOR CUFF INJURY. WHAT YOU CAN DO TO PREVENT SHOULDER INJURIES.
Learning more about Rotator Cuff Injuries.
Understanding Rotator Cuff Injuries
The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles and their tendons that play a crucial role in stabilising and moving the shoulder joint. Injuries to the rotator cuff can cause significant pain and disability, affecting daily activities and athletic performance. Explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for rotator cuff injuries to help you better understand and manage this common condition.
For more information about the Rotator Cuff, click here.
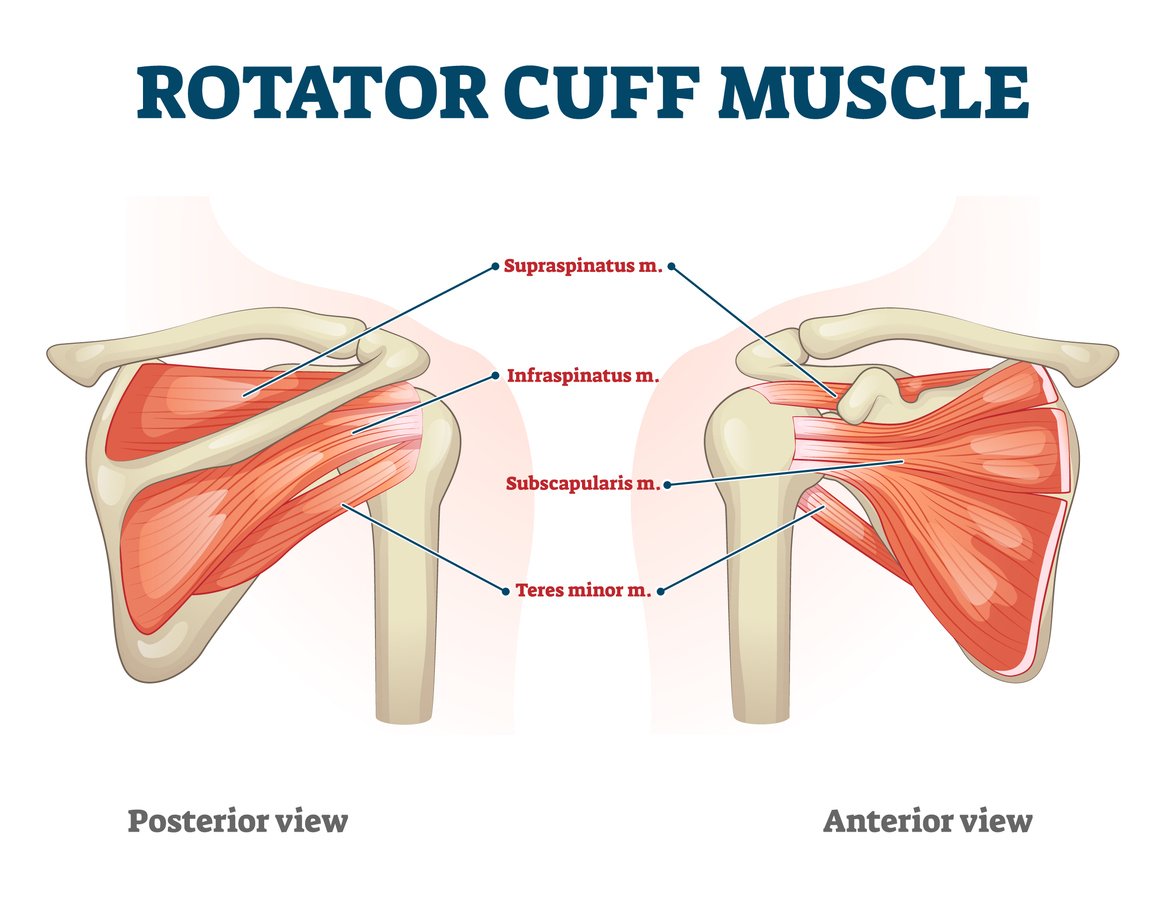
What is the Rotator Cuff?
The rotator cuff consists of four muscles:
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres Minor
Subscapularis
These muscles work together to stabilize the head of the humerus (upper arm bone) within the shallow socket of the shoulder blade and to facilitate arm movements such as lifting and rotating.
Common Causes of Rotator Cuff Injuries
Rotator cuff injuries can result from acute trauma or degenerative changes over time. Some common causes include:
Repetitive Overhead Movements: Activities such as throwing, swimming, and lifting can strain the rotator cuff.
Aging: As we age, the tendons of the rotator cuff can degenerate, making them more prone to injury.
Trauma: Falls or sudden impacts can cause tears or other injuries.
Poor Posture: Chronic poor posture can alter shoulder mechanics, leading to strain and injury.
Overuse: Repetitive stress without adequate rest can cause inflammation and tears.
Types of Rotator Cuff Injuries
Rotator cuff injuries can be classified into several types:
Tendinitis: Inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons, often due to overuse.
Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa (a fluid-filled sac that reduces friction between tissues) in the shoulder.
Partial Tear: Damage to the tendon that does not completely sever it.
Full-Thickness Tear: A complete tear of the tendon, often requiring more intensive treatment.
Symptoms of Rotator Cuff Injuries
The symptoms of a rotator cuff injury can vary depending on the severity of the damage but typically include:
Pain: A dull ache deep in the shoulder, often worsening with movement or at night.
Weakness: Difficulty lifting the arm or performing overhead activities.
Limited Range of Motion: Stiffness and difficulty moving the shoulder.
Clicking or Popping: Sounds during shoulder movement, indicating tendon involvement.
Diagnosing Rotator Cuff Injuries
If you suspect a rotator cuff injury, it’s important to seek medical evaluation. A healthcare provider may use the following methods to diagnose the condition:
Physical Examination: Assessing range of motion, strength, and areas of tenderness.
Imaging Tests: X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI scans can help visualize the extent of the injury.
Special Tests: Specific maneuvers to test the function of the rotator cuff muscles.
Rotator Cuff Muscles
Treatment Options for Rotator Cuff Injuries
The treatment for rotator cuff injuries depends on the severity of the injury and the patient’s overall health and activity level. Common treatment options include:
1. Conservative Treatments
Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that aggravate the injury.
Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying ice to reduce inflammation and heat to relax muscles.
Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to manage pain and inflammation.
Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen the shoulder muscles and improve range of motion.
Corticosteroid Injections: Reducing inflammation and pain in severe cases.
2. Surgical Treatments
Arthroscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive surgery to repair the torn tendon.
Open Surgery: Traditional surgery for larger tears or complex repairs.
Tendon Transfer: Using a nearby tendon to replace the damaged rotator cuff tendon.
Shoulder Replacement: In severe cases where the joint is also damaged, a shoulder replacement may be necessary.
Preventing Rotator Cuff Injuries
While not all rotator cuff injuries can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk:
Strengthening Exercises: Regularly perform exercises to strengthen the shoulder and rotator cuff muscles.
Proper Technique: Use proper form during activities and exercises to avoid undue stress on the shoulder.
Warm-Up: Always warm up before engaging in physical activities.
Posture: Maintain good posture to ensure proper shoulder mechanics.
Gradual Progression: Gradually increase the intensity of physical activities to avoid overuse injuries.
Take Home
Rotator cuff injuries are common but can significantly impact your quality of life if not properly managed. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective recovery. If you experience persistent shoulder pain or suspect a rotator cuff injury, seek medical advice to develop an appropriate treatment plan. With proper care and preventive measures, you can maintain shoulder health and continue to enjoy an active lifestyle.
Get In Touch
If you want to learn more about rotator cuff injuries or shoulder injuries, get in touch with JY Exercise Physiology in Upper Mount Gravatt and speak with an Accredited Exercise Physiologist now. Our free consultation provides an opportunity to discuss how I can facilitate your needs.
Call +61 421 967 711